Overview – ISO/IEC 20000-1 Explained
Delivering structured, scalable, and certifiable ITSM that aligns services to business goals, strengthens governance, and drives continual improvement.
Looking for help? Get in touch with us
Manage Your Software
Visitor

What is ISO/IEC 20000-1 ?
ISO/IEC 20000-1 is the international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM). It defines the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a Service Management System (SMS).
Unlike frameworks such as ITIL, ISO/IEC 20000-1 is a formal, certifiable standard – giving organisations proof that their ITSM practices meet globally recognised best practices.
Certification demonstrates:
- Services aligned to business goals.
- Strong governance and compliance structures.
- Efficient, measurable, and continually improving service delivery.
The Structure of ISO/IEC 20000-1
The standard is organised into 10 clauses, aligned with the Annex SL structure used across all modern ISO management system standards (e.g., ISO 27001).
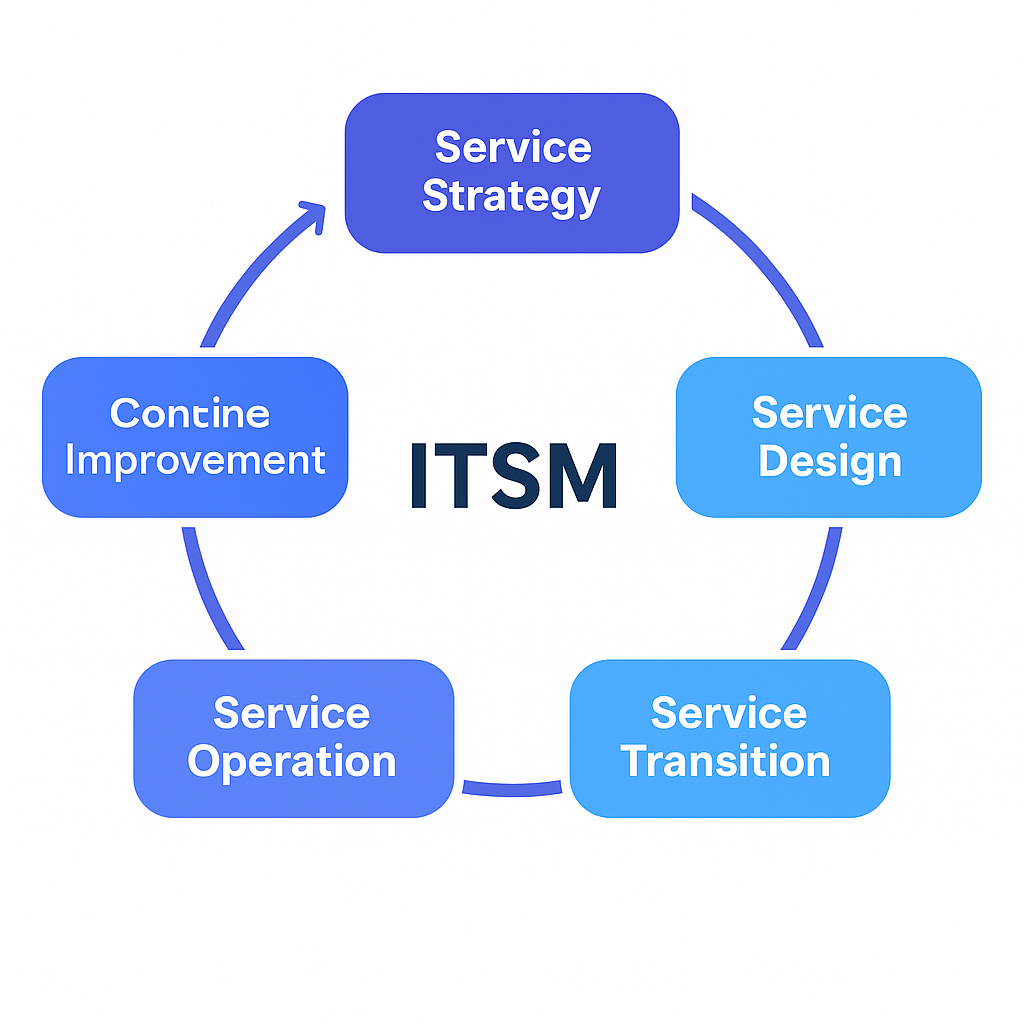
Outlines the purpose of ISO/IEC 20000-1, its alignment with other ISO management standards, and how it provides a framework for establishing a robust Service Management System (SMS).
Defines the applicability of the standard – covering IT-enabled services provided to customers, whether internal or external. The scope sets boundaries for certification, clarifying which parts of the organisation and which services are included.
Lists supporting documents and standards referenced in ISO/IEC 20000-1. This ensures consistency of terminology and interpretation across the industry.
Establishes standardised terminology used throughout ISO/IEC 20000-1. Clear definitions avoid misinterpretation of requirements.
Requires organisations to understand internal and external factors that influence ITSM, including:
- Business objectives and strategy.
- Regulatory and compliance requirements.
- Stakeholders and interested parties.
- Service management scope and boundaries.
Emphasises the role of top management in driving ITSM success. Key requirements include:
- Assigning roles and responsibilities.
- Establishing and communicating the ITSM policy.
- Ensuring commitment, resources, and accountability.
Focuses on proactive planning for service management, covering:
- Risk identification and treatment.
- Setting service management objectives.
- Planning for changes to services or processes.
Defines the resources needed to operate the Service Management System, including:
- Competence and training.
- Awareness and communication.
- Documented information and knowledge management.
The heart of the standard: managing the service lifecycle and ensuring effective processes. This includes:
- Service delivery management.
- Incident, problem, and change management.
- Configuration and asset control.
- Supplier management and service continuity.
Requires organisations to measure and monitor service performance, conduct internal audits, and hold regular management reviews. The goal is to ensure ITSM remains effective and aligned with business needs.
Drives continual service improvement by addressing:
- Nonconformities and corrective actions.
- Identifying opportunities for service enhancements.
- Embedding a culture of continual improvement.
Key Process Areas in ISO/IEC 20000-1 (17 Required)
ISO/IEC 20000-1 requires organisations to implement specific ITSM processes grouped into five categories:
- Planning, control, documented information.
- Service level, capacity, availability, continuity.
- Business relationship management.
- Supplier management.
- Incident management.
- Service request management.
- Problem management.
- Change management.
- Configuration management.
- Information security management.
- Monitoring and reporting.


Key Processes / Practices (20–30 in Practice)
While ISO/IEC 20000-1 specifies 17 required process areas, most organisations adopt 20–30 core processes in their Service Management System. This reflects both ISO compliance and ITIL best practices.
Commonly implemented processes include:
- Incident Management
- Change Management
- Problem Management
- Service Request Management
- Configuration Management
- Service Level Management
- Asset Management
- Capacity & Availability Management
This demonstrates the overlap between ISO/IEC 20000-1 and ITIL 4 – where ISO defines requirements for certification, and ITIL offers a broader library of practices to choose from.
Supporting Parts of ISO/IEC 20000
The standard is supported by additional guidance documents that expand its use:
Part 1 – Requirements for an SMS (mandatory for certification).
Part 2 – Guidance on applying Part 1.
Part 3 – Guidance on scope definition and applicability.
Part 10 – Concepts and vocabulary.
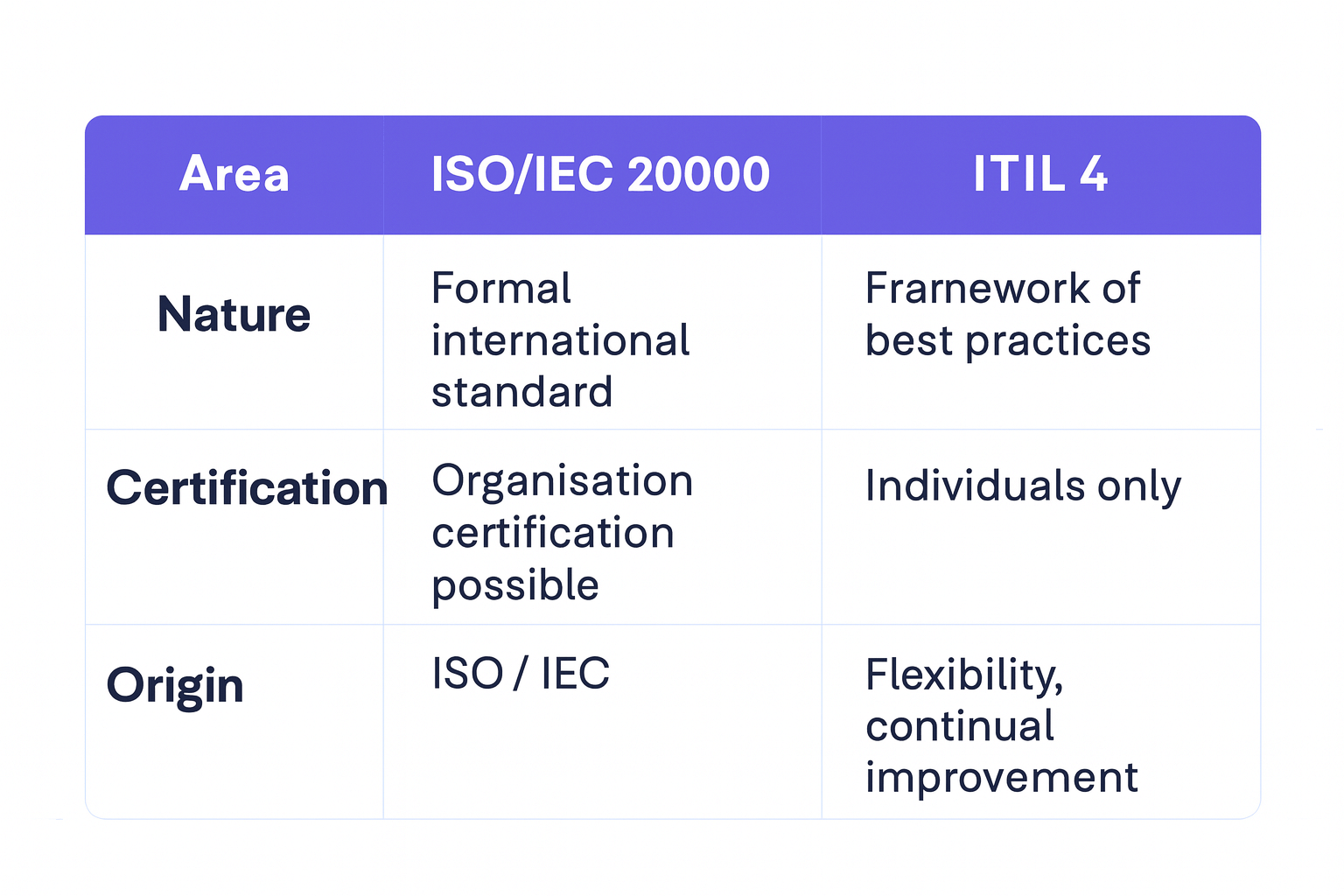
ISO/IEC 20000-1 vs ITIL 4
While ITIL 4 provides flexible best practice guidance, ISO/IEC 20000-1 offers a certifiable framework. Many organisations use them together:
Why ISO/IEC 20000-1 Matters
Implementing ISO/IEC 20000-1 helps organisations to:
- Prove ITSM maturity through global certification.
- Increase efficiency and reduce service delivery costs.
- Strengthen compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Enhance customer confidence and trust.
- Drive continual service improvement.

Calvin Carlo
Manager
Christa Smith
Manager
Jemina Clone
Manager
Smith Vodka
Manager
Cristino Murfi
Manager
Cristino Murfi
ManagerFrequently Asked Questions
generate awareness, drive traffic, connect.
How does it work ?
Do I need a designer to use Techwind ?
What do I need to do to start selling ?
What happens when I receive an order ?
How does it work ?
Ready to strengthen your IT Service Management?
We help organisations design and implement ISO/IEC 20000-1 aligned service management systems that are practical, scalable, and certifiable.






